Everything you need to know about CO2 laser cutters. Learn how they work, what materials they cut, key specifications to compare, and how to choose the right machine for your needs and budget.
What Is a CO2 Laser Cutter?
A CO2 laser cutter uses a carbon dioxide gas mixture to generate a powerful infrared light beam. This beam is focused through mirrors and a lens onto the material surface, vaporizing or burning through it with precision. CO2 lasers have been the workhorse of laser cutting for decades, particularly for non-metal materials.
Unlike mechanical cutting tools that physically contact the workpiece, laser cutting is non-contact. This means no tool wear, no clamping forces, and the ability to cut intricate shapes that would be impossible with traditional methods.
How CO2 Lasers Work
Understanding the technology helps you make better buying decisions:
The Laser Tube
The heart of any CO2 laser is the tube filled with carbon dioxide, nitrogen, hydrogen, and helium gases. When electrical current excites this gas mixture, it produces infrared light at a wavelength of 10.6 micrometers. This wavelength is particularly effective at being absorbed by organic materials like wood, acrylic, leather, and fabric.
The Optical Path
Mirrors (typically three) direct the laser beam from the tube to the cutting head. A focusing lens concentrates this beam to a tiny point, achieving power densities high enough to vaporize material. The quality and alignment of these optics directly affects cut quality.
Motion System
The cutting head moves across the work surface using stepper or servo motors, guided by belts, lead screws, or linear rails. More expensive machines use linear rails and servo motors for faster, more accurate movement.
Cooling System
CO2 laser tubes generate significant heat and require cooling. Small machines may use air cooling, but most use water chillers. Proper cooling extends tube life and maintains consistent output power.
Types of CO2 Laser Cutters
Desktop Machines (40-60W)
Work area: Typically 12" x 8" to 24" x 16"
Best for: Hobbyists, small crafts, prototyping, small engraving businesses
Capabilities:
- Cut 3mm (1/8") acrylic and wood easily
- Cut 6mm (1/4") materials with multiple passes
- Engrave at reasonable speeds
- Detailed work on smaller items
Limitations:
- Smaller work area restricts project size
- Slower cutting on thicker materials
- Less suitable for production work
Price range: $500-$3,000
Mid-Size Machines (80-130W)
Work area: Typically 24" x 16" to 51" x 35"
Best for: Small businesses, sign makers, production work, professional makers
Capabilities:
- Cut 12mm (1/2") acrylic and wood in single pass
- Much faster cutting speeds
- Handle production volumes
- Larger projects in one piece
Considerations:
- Requires more space (machine + ventilation)
- Higher power consumption
- Larger water chiller needed
Price range: $3,000-$15,000
Industrial Machines (150W+)
Work area: 51" x 35" up to full sheet sizes (4' x 8')
Best for: Manufacturing, high-volume production, thick material cutting
Capabilities:
- Cut 20mm+ acrylic and thick hardwoods
- High-speed production cutting
- Continuous operation durability
- Advanced features (auto-focus, pass-through, camera positioning)
Considerations:
- Significant space and power requirements
- Industrial ventilation needed
- Higher maintenance costs
Price range: $15,000-$50,000+
Key Specifications to Compare
Wattage (Power Output)
Laser power determines cutting capability:
- 40W: 6mm acrylic, 6mm wood (with effort)
- 60W: 10mm acrylic, 10mm wood
- 80W: 12mm acrylic, 15mm wood
- 100W: 15mm acrylic, 20mm wood
- 130W: 20mm acrylic, 25mm wood
- 150W+: 25mm+ acrylic, thick hardwoods
These are guidelines—actual results depend on material density, laser quality, and settings.
Bed Size
Consider your typical and maximum project sizes. It's better to have more space than you think you need. Common sizes:
- 300 x 200mm (12" x 8") - Hobby
- 600 x 400mm (24" x 16") - Small business
- 900 x 600mm (36" x 24") - Professional
- 1300 x 900mm (51" x 35") - Production
- 1600 x 1000mm+ (63" x 40"+) - Industrial
Cutting Speed
Speed depends on material and thickness, but machine capability varies. Look for maximum travel speed specifications, but understand that actual cutting is much slower. Servo-driven machines are faster than stepper-driven ones.
Positioning Accuracy
Typically specified as ±0.01mm for quality machines. This matters for detailed work and consistent repeat cuts.
Z-Axis Travel
Determines the maximum material thickness you can accommodate. Some machines offer pass-through slots for longer pieces.
Materials CO2 Lasers Cut Well
Excellent Performance
- Acrylic (PMMA): Clean, polished edges. Cast acrylic engraves better than extruded.
- Wood: Plywood, MDF, hardwoods, veneers. Dark edge marks add character.
- Leather: Clean cuts, excellent for goods and fashion.
- Fabric: Sealed edges prevent fraying. Great for textiles.
- Paper/Cardboard: Intricate cuts impossible by other means.
- Rubber: Stamp making, gaskets.
- Foam: Packaging, inserts, craft foam.
Good for Engraving Only
- Glass: Surface engraving (fractures, doesn't cut)
- Coated metals: With marking sprays for contrast
- Anodized aluminum: Removes anodizing to reveal metal
- Stone: Surface engraving
Materials to Avoid
- PVC/Vinyl: Releases chlorine gas (toxic and corrosive)
- Polycarbonate: Burns, discolors, doesn't cut cleanly
- ABS: Melts, produces toxic fumes
- HDPE: Melts and warps
- Metals: CO2 wavelength reflects off metal surfaces
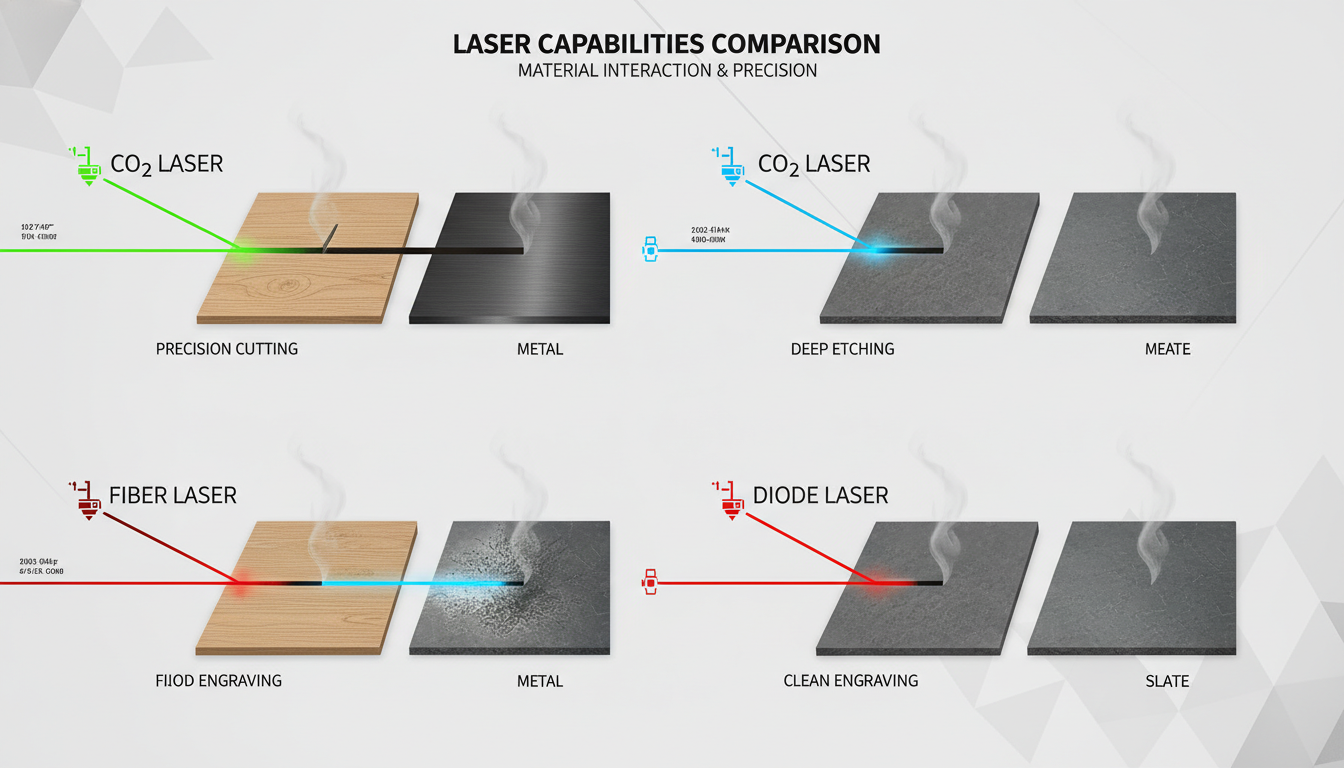
CO2 vs. Fiber vs. Diode Lasers
FeatureCO2FiberDiode Best forOrganic materialsMetalsHobby use Wood/acrylic cuttingExcellentPoorLimited Metal cuttingNoExcellentNo Initial costMediumHighLow Operating costMedium (tube replacement)LowLow Cutting speedFastVery fast (metal)Slow MaintenanceModerateLowLowBottom line: CO2 lasers are the standard for cutting wood, acrylic, leather, fabric, and other organic materials. Fiber lasers are for metal. Diode lasers are entry-level hobby tools.
Price Ranges by Capability
Entry Level ($500-$2,000)
- 40W glass tube lasers
- Smaller work areas
- Basic controllers
- Adequate for learning and hobby use
- May require upgrades for better performance
Prosumer ($2,000-$6,000)
- 60-80W tubes
- Larger work areas
- Better motion systems
- Improved controllers (Ruida, Trocen)
- Suitable for small business use
Professional ($6,000-$15,000)
- 80-130W tubes
- Production-ready build quality
- Linear rail guides
- Better ventilation and safety features
- Reliable for daily commercial use
Industrial ($15,000-$50,000+)
- High-power tubes (130W+)
- Large format capabilities
- RF (metal) tubes available
- Advanced features standard
- Built for continuous production
What to Look for When Buying
Build Quality Indicators
- Steel frame construction (not aluminum extrusions for larger machines)
- Linear rail guides (not wheels on extrusions)
- Quality belts and pulleys
- Proper enclosure with interlocks
- Honeycomb or blade bed included
Important Features
- Air assist: Blows air at cut point—essential for clean cuts
- Red dot pointer: Shows where laser will cut—very helpful
- Adjustable Z-axis: For focusing on different material heights
- Pass-through slots: For cutting longer materials
- Exhaust port: For connecting ventilation
- Water flow sensor: Protects tube from damage
Controller Quality
The controller affects ease of use and capabilities. Ruida controllers are the industry standard for quality Chinese lasers—avoid unknown or no-name controllers. Good controllers offer:
- Reliable file transfer (USB, Ethernet)
- Preview functionality
- Speed/power adjustment
- Position memory
- Compatible with LightBurn software
Sourcing from China with Local Support
The reality of CO2 laser cutters: most machines at every price point are manufactured in China. The difference is in quality control, configuration, support, and service.
Direct Import Challenges
- Quality varies dramatically between factories
- Limited recourse if problems arise
- Shipping damage claims are difficult
- Setup and calibration is your responsibility
- Technical support across time zones and languages
- Parts sourcing for repairs
The Smarter Approach
Working with a US-based supplier who sources from quality Chinese manufacturers gives you:
- Pre-purchase quality verification
- Machines configured for US electrical standards
- Professional setup and training available
- Local technical support
- Warranty backed by a US company
- Parts availability
Ready to Find the Right CO2 Laser Cutter?
Whether you're starting a laser cutting business, adding capabilities to your shop, or upgrading from an entry-level machine, choosing the right CO2 laser cutter is a significant decision.
Contact our team to discuss your specific needs. We'll help you understand what specifications actually matter for your applications and find equipment that fits your requirements and budget.
Browse our laser equipment selection to see what's currently available with full US support.
Ready to get started?
Browse our equipment inventory or get in touch with our team for expert advice on your next project.